
So you’re looking for some fascinating information about animals with cool eyes? Well, look no further! This article is here to provide you with a captivating insight into the world of these unique creatures. From the mesmerizing eyes of peacocks to the mysterious glow of geckos, we’ll explore the astonishingly diverse range of eye-catching features found in the animal kingdom. Prepare to be amazed as we take a closer look at the remarkable animals that have truly mastered the art of eye-catching!
Mantis Shrimp
Overview and species of Mantis Shrimp
When it comes to creatures with fascinating eyes, the Mantis Shrimp is definitely at the top of the list. Known for its vibrant colors and impressive hunting skills, the Mantis Shrimp is a unique marine animal found in tropical and subtropical waters. There are two main species of Mantis Shrimp: the smashing species and the spearer species. The smashing species, as the name suggests, has club-like appendages that it uses to deliver powerful blows to prey, while the spearer species has long, spiky appendages to impale its victims. These species have distinct eye structures that play a crucial role in their remarkable hunting abilities.
Unique features of Mantis Shrimp eyes
The eyes of Mantis Shrimp are truly extraordinary. They possess one of the most complex visual systems found in the animal kingdom. Unlike humans who have three types of color receptors (red, green, and blue), Mantis Shrimp have an incredible sixteen or more color receptors. This allows them to see a wide range of colors, including ultraviolet light, which is invisible to the human eye. In addition to their impressive color vision, Mantis Shrimp eyes can also detect polarized light. This means they can perceive the orientation of light waves, allowing them to locate prey and differentiate between objects with incredible precision.
How Mantis Shrimp eyes contribute in their survival
The remarkable eyes of Mantis Shrimp are vital for their survival. Their ability to see a wide spectrum of colors helps them to navigate their vibrant coral reef environments and spot potential prey. Their sixteen color receptors enable them to detect subtle color variations, which are crucial for identifying well-camouflaged prey or predators. The ability to detect polarized light is especially useful for Mantis Shrimp when hunting. By distinguishing the polarization patterns of light reflecting off prey, they can accurately assess its distance and position, enabling them to strike with astonishing speed and accuracy. Without their exceptional eyesight, Mantis Shrimp would not be as effective in capturing their prey and defending themselves from predators in their dynamic underwater world.
Owls
Different types of owls
Owls are renowned for their nocturnal habits and silent flight. They belong to the order Strigiformes, which includes over two hundred species distributed across the globe. Some of the most well-known owl species include the Barn Owl, Snowy Owl, Great Horned Owl, and the famous Hedwig, the Snowy Owl from the Harry Potter series. Each species possesses unique characteristics, including diverse eye adaptations that suit their specific hunting strategies and habitats.
Distinct characteristics of owl eyes
One of the most striking features of owls is their large, forward-facing eyes. Unlike most birds, owls have eyes positioned at the front of their heads, providing them with binocular vision, just like humans. This allows them to accurately judge distances and precisely locate their prey, even in low-light conditions. Additionally, owl eyes are incredibly large compared to their body size, with some species having eyes that make up over two percent of their total body weight. These enlarged eyes capture as much light as possible, enhancing their ability to see in the dark.
Adaptation and survival usage of owl eyes
Owls are mostly nocturnal hunters, relying on their exceptional eyesight to locate and catch their prey in the dark. The large size of their eyes, combined with a high density of light-sensitive cells called rods, enables them to gather and process even the faintest light. This adaptation makes owls highly efficient night hunters, able to detect prey that may be completely invisible to other animals. With their forward-facing eyes and incredible depth perception, owls can accurately pinpoint the exact location of their prey, even from a considerable distance. The adaptations of their eyes greatly contribute to their survival, allowing them to thrive and dominate the night skies as skilled hunters.
This image is property of static.scientificamerican.com.
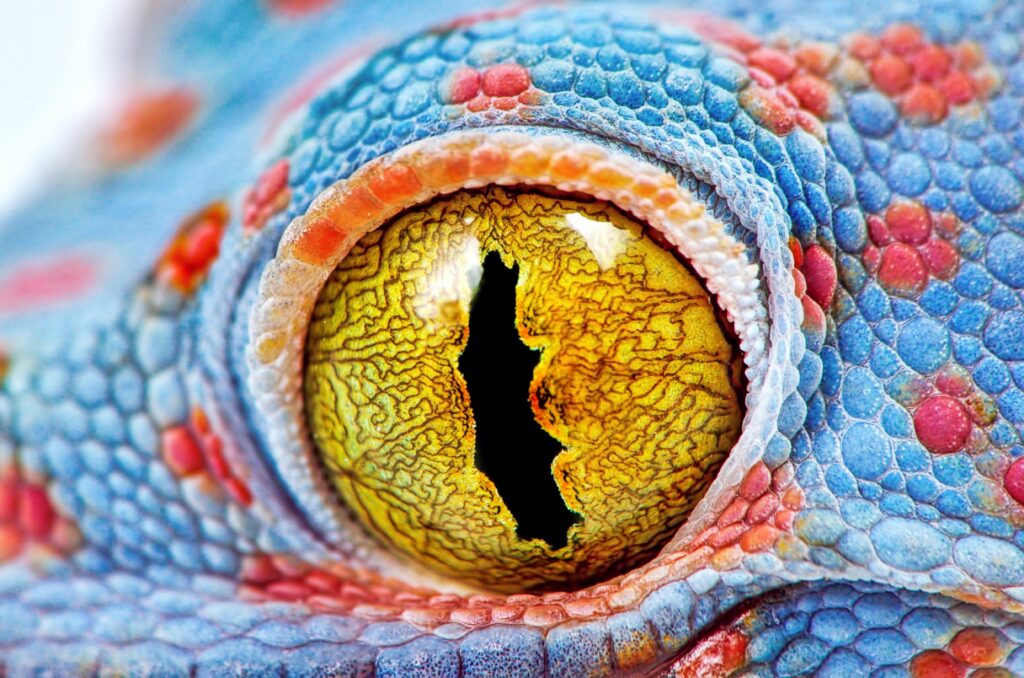
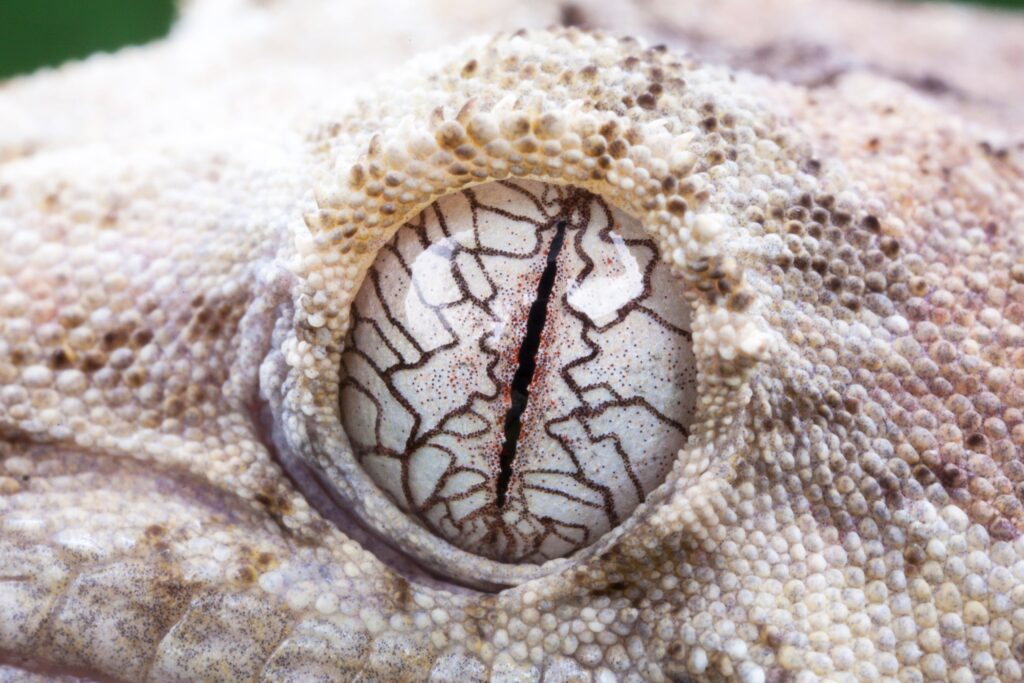
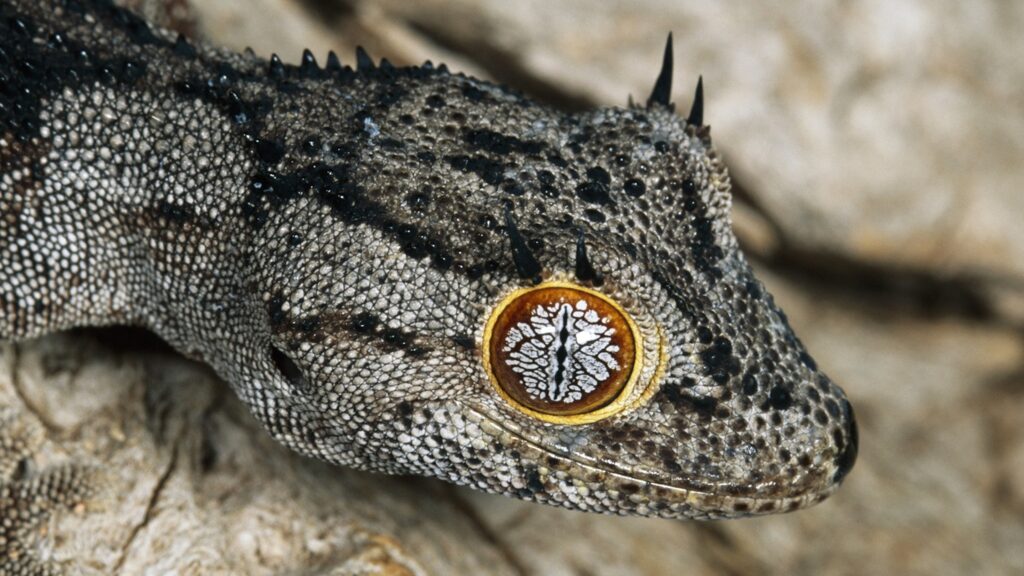
Geckos
Gecko species and their habitats
Geckos are a diverse group of reptiles belonging to the lizard family. There are over 2,000 known species of geckos, inhabiting a wide range of environments across the globe, from tropical rainforests to deserts. Some well-known gecko species include the Leopard Gecko, Tokay Gecko, and the Flying Gecko. Each species has unique adaptations, including their eyes, that help them thrive in their respective habitats.
Unique features of gecko eyes
Geckos have evolved eyes that enable them to navigate their surroundings and locate prey with precision. One of the most notable features of gecko eyes is their ability to see in the dark, much like owls. The pupils of gecko eyes are large and can dilate to capture as much light as possible, allowing them to hunt effectively during nighttime. Additionally, geckos have a keen color vision, which helps them identify food sources, mates, and potential threats.
Role of gecko’s eyes in their daily life and survival
The eyes of geckos play a vital role in their daily life and survival. Their ability to see in low-light conditions allows them to remain active during the night, where they can find food and avoid predators under the cover of darkness. Their keen color vision assists them in identifying ripe fruits, flowers, and insects – the main components of their diet. Furthermore, geckos have a unique ability to see ultraviolet light. This allows them to detect patterns on leaves, flowers, and other surfaces that are invisible to humans and many other animals. The ability to perceive ultraviolet patterns aids geckos in camouflage, communication, and mate selection. Overall, gecko eyes are finely-tuned instruments that contribute significantly to their survival and success in their various habitats.
Dragonflies
Overview of dragonfly species
Dragonflies are enchanting insects belonging to the order Odonata, which also includes damselflies. With their colorful bodies, delicate wings, and incredible flying skills, dragonflies have captivated human attention for centuries. There are over 5,000 known species of dragonflies, inhabiting diverse habitats all around the world, except in extreme cold regions. Their eyes, like many other insects, possess unique characteristics that set them apart.
Special characteristics of dragonfly eyes
Dragonflies have mesmerizing compound eyes that cover a large portion of their head. These compound eyes consist of thousands of individual visual units called ommatidia. Each ommatidium functions as a separate visual receptor, allowing the dragonfly to perceive its surroundings with a wide field of view. Additionally, dragonfly eyes are immensely sensitive to motion, making them excellent predators in the air. The arrangement of the ommatidia provides them with exceptional depth perception, aiding them in accurately estimating distances and tracking prey in-flight.
Importance of eyes for Dragonfly’s flying skill and survival
The unique eyes of dragonflies are crucial for their flying skills and survival. The wide field of view provided by their compound eyes allows them to detect movement in almost every direction, giving them an advantage when hunting or evading predators. Dragonflies are incredibly agile fliers, and their precise depth perception, facilitated by their eyes, enables them to make quick and accurate maneuvers in mid-air. Their acute vision also helps them spot potential mates during elaborate courtship displays, ensuring successful reproduction. Without their remarkable eyesight, dragonflies would not be able to perform their extraordinary aerial feats or flourish as incredible predators in the insect world.

This image is property of s3.amazonaws.com.
Tarsiers
Different kinds of tarsiers
Tarsiers are unique and captivating primates that belong to the family Tarsiidae. They are small, nocturnal creatures found in Southeast Asia, particularly in Indonesia, the Philippines, and Borneo. There are around thirteen known species of tarsiers, each possessing distinct characteristics, including their remarkable eyes.
Special features of tarsier eyes
The most striking feature of tarsiers is their disproportionately large eyes compared to their body size. In fact, tarsiers have the largest eye-to-body ratio of any known mammal, allowing them to have exceptional vision even in low-light conditions. This adaptation is ideal for their nocturnal lifestyle, as they rely heavily on their eyes to navigate their dense forest habitats and locate their prey with accuracy. Additionally, tarsiers have elongated, flexible necks that can rotate their heads almost 180 degrees, giving them an impressive field of view.
Role of tarsier’s eyes in hunting and survival
The large, round eyes of tarsiers are critical for their hunting and survival in the dense forests they call home. Their incredible night vision enables them to efficiently locate and capture insects and small vertebrates, which make up the majority of their diet. The high sensitivity of their eyes to low levels of light allows them to see prey that would be practically invisible to other animals. Tarsiers’ eyes also aid in detecting and evading potential predators, as their sharp vision and wide field of view provide early warning signs of danger. The unique eyes of tarsiers are essential tools for their survival, allowing them to adapt and thrive in the complex and challenging environments they inhabit.
Cuttlefish
Different types of Cuttlefish
Cuttlefish are fascinating marine creatures that belong to the same family as squids and octopuses, known as cephalopods. There are over 100 known species of cuttlefish, found in various oceans and seas around the world. Each species possesses distinctive characteristics, including their remarkable eyes.
Unusual characteristics of Cuttlefish eyes
Cuttlefish have eyes that are quite different from those of most other animals. Their eyes are large, round, and highly mobile, allowing them to scan their surroundings and quickly focus on potential prey or threats. One of the extraordinary features of cuttlefish eyes is their ability to change color and pattern. Cuttlefish can alter the shape of specialized pigment cells called chromatophores in their skin, enabling them to blend seamlessly into their environment. This remarkable color-changing ability is controlled by their eyes and helps them camouflage themselves from predators and ambush prey.
Contribution of eyes in Cuttlefish protection mechanism
The eyes of cuttlefish play a crucial role in their protective mechanisms. Their ability to change color and pattern allows them to blend into their surroundings and avoid detection by predators or prey. By closely monitoring their environment through their eyes, cuttlefish can adapt their skin color and pattern to match specific backgrounds, making them virtually invisible. This evolutionary adaptation has enabled cuttlefish to become highly effective ambush predators. Additionally, the large size and mobility of their eyes provide them with excellent visual awareness, ensuring they can detect potential threats and react swiftly to changing circumstances. Cuttlefish eyes are integral to their survival, enabling them to thrive and adapt in the ever-changing underwater world they inhabit.

This image is property of static.scientificamerican.com.
Goats
Characteristics of goat species
Goats are versatile and hardy mammals that are found in various environments worldwide, from mountains to deserts. There are over 300 different breeds of goats, each with its unique characteristics and adaptations. One notable feature of goats is their eye pupil, which sets them apart from many other animals.
Uniqueness of goat eye pupil
The eyes of goats are known for their striking horizontal rectangular pupils. Unlike most animals with circular or vertically elongated pupils, goats have pupils that are horizontally elongated. This unique eye shape provides them with several advantages in their daily lives. The horizontal pupil allows goats to have a panoramic field of view, excellent depth perception, and an increased range of peripheral vision. This adaptation gives them a wider visual range, which aids in the detection of potential predators and helps them navigate different terrains more effectively.
Adaptation and benefits of goat’s unique eyes
The unusual eye pupil shape in goats is an evolutionary adaptation that benefits their survival. The panoramic field of view allows goats to spot approaching predators from various angles, mitigating the risk of surprise attacks. Their excellent depth perception enables them to accurately assess distances, which is especially important when navigating rocky or uneven terrain. The increased range of peripheral vision allows goats to keep a watchful eye on their surroundings, providing them with early warning signs of potential danger. Additionally, by having horizontal pupils, goats can better compensate for movement while maintaining a stable visual field. This adaptability contributes significantly to their agility and sure-footedness, allowing them to navigate steep mountain slopes and rough terrains with ease. The distinctive eyes of goats are a remarkable adaptation that enhances their survival and success in a variety of environments.
Colossal Squid
Description and habitat of Colossal Squid
The colossal squid, scientifically known as Mesonychoteuthis hamiltoni, is one of the most mysterious and elusive creatures of the deep sea. As its name suggests, it is truly colossal, with females reaching lengths of up to 14 meters (46 feet). This remarkable creature inhabits the deep, icy waters of the Southern Ocean, mainly found near Antarctica. The colossal squid possesses unique features, including its eyes, that aid in its survival in the extreme conditions of the deep sea.
Exceptional size and features of Colossal Squid eyes
The eyes of the colossal squid are the largest known eyes in the animal kingdom. Measuring up to 27 centimeters (11 inches) in diameter, these eyes are as big as dinner plates. The size of their eyes is a result of living in the extreme depths of the ocean, where only faint traces of light can penetrate. Large eyes allow colossal squid to maximize their sensitivity to detect even the faintest bioluminescent light emitted by other deep-sea creatures. Additionally, the eyes have a unique lens structure that enables them to gather and focus scarce light effectively.
Role of Squid’s eyes in deep-sea survival
The colossal squid’s enormous eyes are essential for its survival in the depths of the ocean. In the pitch-black environment of the deep sea, where sunlight cannot penetrate, the ability to detect any faint traces of light is crucial. The large size of their eyes allows them to capture as much of this scarce light as possible, enhancing their ability to navigate their surroundings and locate potential prey. The unique lens structure of their eyes further optimizes their light-gathering capabilities, ensuring they can make the most of the limited light available. The eyes of the colossal squid are a testament to the incredible adaptations required to survive in the extreme conditions of the deep sea, where visibility is almost non-existent.

This image is property of i.natgeofe.com.
Chameleons
Overview of Chameleon species
Chameleons are a fascinating family of reptiles renowned for their ability to change color and their distinctive eye structures. They belong to the family Chamaeleonidae and are found predominantly in Africa, Madagascar, and parts of southern Europe and Asia. Chameleons have evolved several unique characteristics, including their specialized eyes, which play a crucial role in their hunting and survival strategies.
Distinctive features of Chameleon eyes
Chameleons have some of the most extraordinary eyes in the animal kingdom. One of their most distinctive features is their independently mobile eyes, which can rotate and move independently of each other. This allows chameleons to have a 360-degree field of vision without moving their bodies. Additionally, chameleons have cone-shaped, bulging eyes that provide them with exceptional depth perception and the ability to judge distance accurately. Their eyes are also incredibly large in proportion to their body size, aiding them in their keen visual awareness.
Importance of Chameleon’s eyes in hunting and survival
The specialized eyes of chameleons are vital for their hunting and survival strategies. The ability to move their eyes independently gives them an unparalleled field of view, allowing them to monitor their surroundings for potential threats or prey from multiple angles simultaneously. This gives them a significant advantage while hunting, enabling them to patiently observe their target or scan for insects, their primary food source. The bulging shape and large size of their eyes provide exceptional depth perception, assisting them in accurately calculating distances, which is crucial when launching their lightning-fast, accurate tongue strikes to capture prey. Chameleon eyes also contribute to their intricate signaling and communication behaviors. By changing the color, pattern, or position of their eyes, chameleons can convey various messages to other chameleons, including aggression or readiness to mate. The remarkable eyes of chameleons are an essential component of their survival toolkit, allowing them to excel in their unique arboreal habitats and maintain their enigmatic reputation.
Four-Eyed Fish
Habitat and types of Four-Eyed Fish
The Four-Eyed Fish, scientifically known as Anableps, is a unique species of fish found in freshwater habitats of Central and South America. Contrary to its name, this fish does not actually have four eyes but instead possesses a remarkable adaptation in its visual structure. There are four recognized species of Four-Eyed Fish, each inhabiting different regions and bodies of water within their native range.
Unique characteristics of Four-Eyed Fish eyes
The Four-Eyed Fish has eyes that are divided into two distinct parts, allowing them to exploit both the underwater and above-water environments effectively. The upper half of each eye is adapted to see above the waterline, while the lower half is optimized for underwater vision. This unique eye structure helps the Four-Eyed Fish to detect prey and threats across the water-air interface without compromising their underwater vision. It also allows them to conserve energy by focusing on the relevant visual information for their immediate environment.
Survival and hunting benefits of Four-Eyed Fish’s eyes
The divided eyes of the Four-Eyed Fish contribute significantly to its survival and hunting strategies. By having the ability to see above and below the water’s surface simultaneously, they can detect potential predators or prey accurately. This adaptation gives the fish an advantage in evading aerial predators while remaining submerged or seeking food at the water’s surface. The ability to focus on the necessary visual information for their immediate environment allows them to efficiently allocate their energy towards capturing prey or avoiding danger. The unique eyes of the Four-Eyed Fish exemplify the remarkable evolutionary adaptations that allow them to thrive in the challenging aquatic ecosystems they inhabit.
In conclusion, animals with cool eyes exhibit remarkable adaptations and unique visual structures that aid in their survival and hunting strategies. From the complex eyes of Mantis Shrimp, providing exceptional color vision and the ability to detect polarized light, to the horizontally elongated pupils of goats, enhancing their field of view and depth perception, each species has evolved eyes perfectly suited to their environment. Whether it’s the extraordinary eyesight of owls adapted for hunting in the dark, the large, round eyes of tarsiers enabling exceptional night vision, or the enormous eyes of the colossal squid optimized for deep-sea detection, these animals showcase the diversity and ingenuity of the natural world’s visual systems. Each species’ eyes are a testament to the incredible adaptations and evolutionary pathways that have allowed these animals to excel in their respective habitats and ensure their survival for generations to come.




