
Imagine a world where plants hold secrets that surpass the capabilities of any animal. Curiosity piqued? Look no further than the revolutionary product, “What Can Plants Do That Animals Cannot.” This groundbreaking exploration sheds light on the extraordinary abilities of plants. From harnessing the power of photosynthesis to communicating through chemical signals, this article unveils the fascinating realm of plant life that will leave you in awe of nature’s wonders. Get ready to challenge everything you thought you knew about the natural world.
This image is property of lh4.googleusercontent.com.
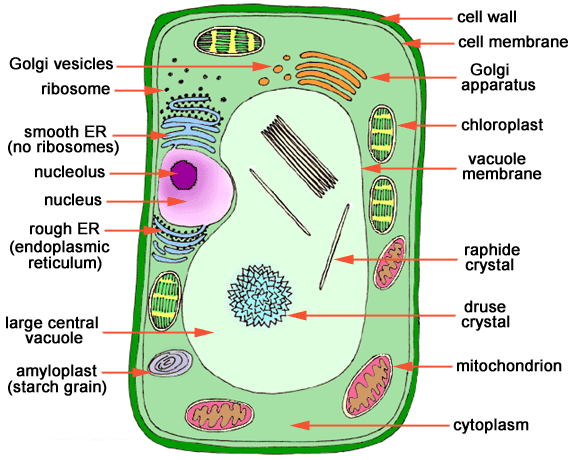
1. Photosynthesis
Plants have the remarkable ability to perform photosynthesis, a process that converts sunlight into energy. This process involves the absorption of sunlight by chlorophyll, a pigment found in plant leaves, and the production of glucose and oxygen. Photosynthesis allows plants to generate their own food, making them self-sustainable organisms. This incredible feature sets plants apart from animals, as animals are unable to produce their own nutrition through photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis: A Source of Energy
Through photosynthesis, plants are able to convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into glucose, a form of sugar that serves as their main source of energy. This energy fuels all the metabolic processes within the plant, allowing it to grow, develop, and carry out essential functions. In contrast, animals rely on consuming other organisms or plant products for nourishment, as they lack the ability to produce their own energy through photosynthesis.
Oxygen Production
Aside from providing plants with energy, photosynthesis also results in the release of oxygen into the atmosphere. During photosynthesis, plants absorb carbon dioxide from the air and release oxygen as a byproduct. This process not only sustains the plants themselves but also plays a crucial role in maintaining the oxygen levels necessary for animal life on Earth. Without plants’ ability to produce oxygen through photosynthesis, life as we know it would not be possible.
2. Cell Wall
Another feature that sets plants apart from animals is the presence of a cell wall. While animals have cell membranes, plants have an additional layer called the cell wall that surrounds each of their cells. Made primarily of cellulose, the cell wall provides structural support and protection to plant cells.
Structural Support
The cell wall’s main function is to maintain the structural integrity of plant cells and provide support to the entire plant. It allows plants to grow upward, against gravity, by providing strength and rigidity. This is one of the reasons why plants can grow to such great heights, while animals remain limited in size due to the absence of a cell wall.
Protection
In addition to providing structural support, the cell wall also acts as a protective barrier for plant cells. It helps defend against physical damage, pathogens, and pests. The strong and rigid nature of the cell wall provides a physical barrier that makes it more challenging for harmful microorganisms to invade plant cells, giving plants a higher level of protection compared to animals.
This image is property of 2.bp.blogspot.com.
3. Growth and Regeneration
Plants exhibit an exceptional capacity for growth and regeneration, a characteristic that is unmatched by animals.
Continuous Growth
Unlike most animals that reach a certain size at adulthood and stop growing, plants have the ability to continue growing throughout their entire lifespan. This is achieved through the activity of meristems, which are regions of undifferentiated cells that can continuously divide and differentiate into different types of plant tissues. As a result, plants can grow in response to environmental conditions, such as the availability of sunlight, water, and nutrients.
Regeneration
Plants also possess the astounding ability to regenerate lost or damaged parts. If a plant’s stem or leaf is injured or removed, it has the potential to grow back and replace the lost tissue. This regenerative capacity allows plants to recover from damage and continue their growth and development, making them highly resilient organisms.
4. Dormancy
Plants have the ability to enter a dormant state, where they reduce their metabolic activities and conserve resources during unfavorable environmental conditions.
Surviving Harsh Conditions
During periods of drought, extreme temperatures, or lack of sunlight, plants can enter dormancy to minimize water loss, energy consumption, and damage caused by environmental stressors. In this state, plants become less active and slow down their growth and development until conditions improve. Animals, on the other hand, are unable to enter such a state and must actively seek out suitable habitats or adapt to changing circumstances.
Conservation of Resources
Dormancy allows plants to conserve vital resources, such as water and nutrients, during times when these resources may be scarce. By reducing metabolic activities, plants can allocate their limited resources more efficiently, ensuring their survival until more favorable conditions arise. This ability to enter dormancy and conserve resources sets plants apart from animals, as animals are constantly engaged in active metabolic processes regardless of environmental conditions.

This image is property of slideplayer.com.
5. Reproduction
Plants exhibit a wide variety of reproductive strategies, ranging from asexual reproduction to complex processes involving flowers, fruits, and seeds.
Asexual Reproduction
Unlike animals that rely primarily on sexual reproduction, plants have the ability to reproduce asexually. Through processes such as vegetative propagation, where new plants are produced from specialized plant structures like stems or roots, plants can generate offspring that are genetically identical to the parent plant. This asexual reproduction allows plants to quickly colonize new areas or propagate desirable traits without the need for a partner.
Sexual Reproduction
In addition to asexual reproduction, plants also engage in sexual reproduction. This involves the production of flowers, which contain reproductive organs such as the male stamen and the female pistil. Pollination occurs when pollen grains are transferred from the stamen to the pistil, leading to fertilization and the eventual formation of seeds. This reproductive strategy allows for genetic diversity and adaptation to changing environmental conditions, enabling plants to survive and thrive in various habitats.
6. Environmental Adaptation
Plants have an impressive ability to adapt to diverse environmental conditions, allowing them to inhabit a wide range of habitats around the world.
Tolerance to Environmental Factors
Plants can tolerate and adapt to extreme conditions such as high or low temperatures, drought, high salinity, and poor soil quality. Through various mechanisms, such as adjusting their leaf structure, developing efficient water storage systems, or altering their metabolism, plants can withstand and thrive in environments that would be inhospitable to most animals.
Symbiotic Relationships
Plants also form beneficial relationships with other organisms, such as mycorrhizal fungi, which help improve their nutrient uptake. These symbiotic associations allow plants to access nutrients that may be scarce in their environment, enhancing their ability to adapt and survive.

This image is property of hi-static.z-dn.net.
7. Synthesis of Nutrients
Plants have the ability to synthesize a wide range of essential nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, and organic compounds.
Self-Sufficiency
Unlike animals that rely on external sources for nutrients, plants are self-sufficient when it comes to essential compounds. Through photosynthesis, they can produce carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids, which serve as the building blocks for their growth and development. Additionally, plants have the ability to synthesize vitamins, such as vitamin C and vitamin E, and various secondary metabolites with important roles in defense against pathogens and predators.
Nutritional Value
Plants not only produce essential nutrients for their own growth but also provide a crucial source of nutrition for countless animal species. As primary producers, plants form the base of many food chains, supporting ecosystems and providing sustenance for herbivorous animals. This ability to synthesize a wide array of nutrients makes plants vital for the functioning of ecosystems and the survival of multiple animal species.
8. Longevity
Plants have the potential to live for exceptionally long periods, some even for hundreds or thousands of years.
Long Lifespan
Although individual plant cells have a limited lifespan, plants, as a whole, can exhibit considerable longevity. Some examples include the giant sequoias of North America, which can live for thousands of years, or the bristlecone pines that inhabit the harsh conditions of the White Mountains in California.
Growth Rings
One method used to estimate the age of certain plants is by analyzing their growth rings. Each year, plants typically develop a new growth ring, visible when cutting a tree trunk. By counting these rings, scientists can determine the age of the plant and gain valuable insights into its growth history. This long lifespan surpasses the lifespan of most animals, allowing plants to contribute to the stability and continuity of ecosystems.

This image is property of images.slideplayer.com.
9. Ability to Produce Oxygen
Plants possess an extraordinary ability to produce oxygen through photosynthesis, a process that is essential for the survival of all animals on Earth.
Oxygen as a Byproduct
During photosynthesis, plants absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen as a byproduct. This oxygen is then released into the atmosphere, where it replenishes and maintains the oxygen levels necessary for the respiration of aerobic organisms. Animals, including humans, require oxygen for their metabolic processes, making the production of oxygen by plants a fundamental contribution to maintaining life on our planet.
10. Communication
While plants may not communicate in the same way animals do, they have evolved remarkable methods of exchanging information and responding to their surroundings.
Chemical Signaling
Plants release various chemicals, such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs), to communicate with each other and with other organisms. These chemical signals can convey information about changes in environmental conditions, the presence of pests or pathogens, or even attract pollinators. For example, when a plant is attacked by herbivores, it can release volatile compounds that alert neighboring plants, triggering them to produce defensive compounds that deter the attackers.
Response to External Stimuli
Plants also exhibit tropisms, the growth or movement of an organism in response to a stimulus. For instance, phototropism refers to the bending of plant shoots towards a light source, ensuring optimal light absorption for photosynthesis. Additionally, plants can respond to touch, gravity, and other environmental cues, allowing them to adapt and optimize their growth in their specific habitats.
In conclusion, plants possess a multitude of extraordinary abilities that set them apart from animals. From performing photosynthesis and producing oxygen to having a cell wall and regenerative capacity, plants showcase a remarkable range of features. Their ability to adapt to diverse environments, synthesize essential nutrients, and engage in a variety of reproductive strategies make plants crucial for the functioning of ecosystems and the survival of numerous animal species. Truly, plants are intricately woven into the tapestry of life on Earth, providing us with sustenance, oxygen, and natural beauty.




