
You’re probably aware that humans are distinct from other animals, but have you ever thought about what exactly sets us apart? “What Makes Humans Unique from Other Animals” is a fascinating exploration of the characteristics that make humans stand out in the animal kingdom. This thought-provoking article delves into the complex combination of traits, such as advanced cognition, complex language, and cultural diversity, that contribute to our exceptional nature. Prepare to be amazed as you discover the remarkable qualities that make us truly one-of-a-kind.

This image is property of mediaproxy.salon.com.
Advanced Communication Skills
Development of complex languages
One of the key features that sets humans apart from other animals is our advanced ability to communicate using complex languages. While other animals may have basic forms of communication, such as simple vocalizations or gestures, humans have developed intricate languages with grammar, syntax, and an extensive vocabulary. This allows us to convey complex thoughts, ideas, and emotions to others in a way that is unique in the animal kingdom.
Languages have evolved and developed over thousands of years, allowing for the transmission of knowledge and information across generations. From early spoken languages to written forms, humans have continually expanded and refined their communication skills. The development of language has played a crucial role in human progress, enabling the sharing of ideas, the formation of complex societies, and the advancement of technology.
Use of symbols and abstract thinking in communication
Another aspect of advanced communication skills is the ability to use symbols and engage in abstract thinking. Humans have the capacity to represent objects, ideas, and concepts through symbolic language, allowing us to communicate about things that are not physically present. This ability to represent and manipulate symbols is a fundamental characteristic of human cognition and sets us apart from other animals.
Through the use of symbols, we can convey abstract concepts, emotions, and intentions. For example, words such as “love,” “freedom,” or “justice” are abstract concepts that have meaning and significance to us. We can communicate these ideas to others through language, enabling us to connect on a deeper level and share our thoughts and experiences.
Ability to transmit knowledge across generations
One of the most remarkable aspects of human communication is our ability to transmit knowledge across generations. Through language, humans have developed a system of education and learning that allows us to pass down information from one generation to the next. This transmission of knowledge has played a critical role in human progress and the accumulation of collective wisdom.
From ancient oral traditions to modern educational institutions, humans have developed methods and systems to ensure that knowledge and skills can be preserved and passed on to future generations. This ability to communicate and transmit knowledge has allowed humans to build upon the discoveries and achievements of those who came before us, leading to continuous advancements in various fields, such as science, technology, and the arts.
The Capability for Complex Emotions
Unique emotional depth such as empathy, jealousy, shame
While many animals experience emotions to some degree, humans possess a unique emotional depth and range that sets us apart. Humans are capable of experiencing complex emotions such as empathy, jealousy, shame, and awe, which require a higher level of cognitive processing. These emotions shape our relationships, behaviors, and decision-making processes in ways that are distinct from other species.
Empathy, for instance, allows humans to understand and share the feelings and perspectives of others. It enables us to connect with one another on a deeper level, fostering compassion and cooperation. Jealousy and shame are emotions that arise from our awareness of social norms and expectations, highlighting our unique capacity for self-reflection and evaluation.
Cross-cultural emotions and expressions
Another fascinating aspect of human emotions is the cross-cultural variation in emotional experiences and expressions. While some emotions, such as happiness or sadness, may be universally understood, others can be influenced by cultural and social factors. Different cultures may have distinct norms and rules surrounding emotions, leading to variations in how emotions are recognized, expressed, and regulated.
For example, the concept of “face” in East Asian cultures emphasizes the importance of social reputation and avoiding public embarrassment. This cultural value may shape how individuals in these cultures express and regulate their emotions. Understanding these cross-cultural variations in emotions is essential for effective communication and building positive relationships across different cultural contexts.
Role of emotions in human decision making and behavior
Emotions play a significant role in human decision making and behavior. Our emotional responses can influence the choices we make, the actions we take, and the interactions we have with others. Emotions can motivate us to pursue certain goals, guide our moral judgments, and shape our social relationships.
For instance, fear can prompt us to avoid dangerous situations, while love can lead us to form lasting bonds with others. Emotions also serve as signals to communicate our needs and intentions to others. By interpreting and responding to the emotional cues of those around us, we can navigate social interactions and build meaningful connections.
Understanding the complex interplay between emotions, cognition, and behavior is crucial for comprehending human nature and the factors that drive our actions. It highlights the intricate relationship between our cognitive abilities and our emotional experiences, setting humans apart from other animals.
Self-Awareness and Consciousness
Understanding of self and personal identity
One of the defining characteristics of human beings is our ability to understand ourselves and develop a sense of personal identity. Humans possess self-awareness, the capacity to recognize ourselves as separate entities from others and to have an introspective understanding of our thoughts, emotions, and actions.
This self-awareness allows us to reflect on our own experiences, motivations, and values, and to develop a sense of who we are as individuals. It enables us to have a sense of agency, to make conscious choices, and to take responsibility for our actions. This level of self-awareness is not found to the same extent in other animals, setting humans apart in their ability to engage in self-reflection and self-evaluation.
Awareness and interpretation of others’ emotions and intentions
Alongside self-awareness, humans possess the ability to recognize and interpret the emotions and intentions of others. This social cognition allows us to understand and navigate complex social interactions, fostering cooperation, empathy, and collaboration.
By observing facial expressions, body language, and vocal cues, humans can decipher the emotional states of others, gaining insights into their thoughts, feelings, and needs. This ability to understand and respond to others’ emotions is critical for building strong interpersonal relationships and effective communication.
The concept of mortality and existential questioning
Another aspect of human consciousness that sets us apart from other animals is our awareness of mortality and our capacity for existential questioning. Humans are unique in their ability to contemplate their own mortality and to grapple with existential questions about the nature of life, purpose, and meaning.
This reflective capacity gives rise to philosophical and spiritual inquiries, as well as artistic expressions that explore the complexities of human existence. Humans have devised various belief systems, rituals, and cultural practices to cope with the existential quandaries that arise from our awareness of our own finitude.
The concept of mortality and the pursuit of meaning and purpose are fundamental aspects of human consciousness that distinguish us from other animals. This capacity for deep introspection and contemplation is a significant driver of human creativity, curiosity, and intellectual pursuits.
Tool Use and Technological Innovation
Early tool use in human history
Humans have a long history of using tools, which sets us apart from other animals. Tool use dates back millions of years and has played a crucial role in our evolution and survival. Early humans fashioned tools from stones, bones, and other materials to enhance their ability to hunt, gather food, build shelters, and defend themselves.
Tool use was not only a manifestation of human intelligence but also a means to adapt to different environments and challenges. Over time, humans refined their tool-making techniques, developing more sophisticated and specialized tools. This capacity to create and utilize tools signified a significant shift in our evolutionary trajectory.
Technological advancements and their impact on human evolution
Throughout human history, technological advancements have propelled our evolution and shaped our societies. From the invention of the wheel to the modern digital age, humans have continuously developed and harnessed new technologies to improve our lives.
Technological innovations have revolutionized agriculture, transportation, communication, medicine, and countless other domains. These advancements have increased our ability to meet our basic needs, solve complex problems, and connect with others across vast distances. They have transformed the way we live, work, and interact, underscoring our unique capacity for innovation and adaptation.
Human reliance on tools and technology in everyday life
In contemporary society, humans have become increasingly reliant on tools and technology in everyday life. From smartphones and computers to medical devices and transportation systems, technology surrounds us and shapes our experiences. It has become an integral part of our daily routines and has profoundly influenced how we work, communicate, and navigate the world.
This reliance on tools and technology highlights our ability to develop and use external resources to extend our capabilities. By leveraging technological innovations, humans have exponentially increased their productivity and efficiency. However, it also raises questions about the potential drawbacks and ethical considerations associated with our reliance on technology.

This image is property of cdn.britannica.com.
Cultural Adaptation and Diversity
Development of diverse cultural practices and societies
A defining characteristic of humans is our remarkable ability to adapt to different environments and develop diverse cultural practices and societies. Humans have created a wide range of cultural norms, rituals, beliefs, and customs that vary across different regions and social groups.
Cultural adaptation allows humans to thrive in various ecological niches and cope with the challenges posed by different environments. Our capacity to adapt extends beyond physical survival to encompass social, psychological, and symbolic dimensions. Cultural practices serve as a means to transmit knowledge, maintain social cohesion, and express collective identities.
Cultural impact on human behavior and perspective
Culture has a profound impact on human behavior and perspective. It shapes our values, beliefs, attitudes, and expectations, influencing how we perceive and interpret the world around us. Different cultures may prioritize and emphasize distinct aspects of life, such as individualism versus collectivism, hierarchical versus egalitarian structures, or secular versus religious beliefs.
Cultural factors also influence our language, communication styles, social norms, and moral frameworks. By understanding the role of culture in shaping human behavior and perspective, we can appreciate the diversity of human experiences and foster cross-cultural understanding and cooperation.
Importance of culture in human survival and progress
Culture plays a critical role in human survival and progress. Through cultural practices, humans have developed strategies for adapting to various environments, harnessing natural resources, and organizing social systems. Cultural knowledge and innovations have been passed down through generations, enabling humans to build upon previous achievements and continually advance.
Culture also provides a sense of identity, belonging, and purpose. It strengthens social bonds and facilitates cooperation within communities. Additionally, cultural expressions, such as art, music, literature, and dance, serve as a means to preserve and communicate shared human experiences and values.
The importance of culture in human life underscores our capability for social learning, creativity, and collective problem-solving, setting us apart from other animals.
Reliance on Social Structures
Complex social organization in human societies
Humans have evolved intricate social structures that set us apart. Unlike many other animal species, humans have developed complex societies characterized by hierarchies, rules, and roles. We live in communities, tribes, and nations, creating diverse systems of social organization that shape our interactions, behaviors, and identities.
These social structures provide a framework for cooperation, conflict resolution, division of labor, and resource distribution. They also enable us to form cohesive groups, establish shared norms, and work towards common goals. The development of complex social organization reflects our unique capacity for cooperation, communication, and collective problem-solving.
Role of family and community in human upbringing
The family and community play pivotal roles in human upbringing and socialization. Humans have prolonged childhoods and depend on caregivers and social interactions for survival, learning, and emotional development. This extended period of dependency allows for the transmission of cultural knowledge, socialization into societal norms, and the development of social bonds.
Families provide emotional support, nurturance, and guidance to their members, fostering the development of important social and cognitive skills. Communities further contribute to the socialization process, providing a broader network of relationships and opportunities for learning from others. The interactions within families and communities shape our beliefs, values, and behaviors, influencing our identities and roles within society.
Influence of societal norms and rules on human behavior
Societal norms and rules have a significant influence on human behavior. Humans are social beings who internalize and adhere to the norms and expectations of their communities. These norms guide our behaviors, interactions, and decision-making processes, ensuring social order, cooperation, and cohesion.
Social norms can vary across cultures and communities, reflecting the values, beliefs, and priorities of each group. They define acceptable behaviors, moral standards, and social roles. Humans not only comply with existing norms but also contribute to the evolution and adaptation of societal norms over time. Our ability to create, challenge, and transform social norms demonstrates our capacity for social change and progress.
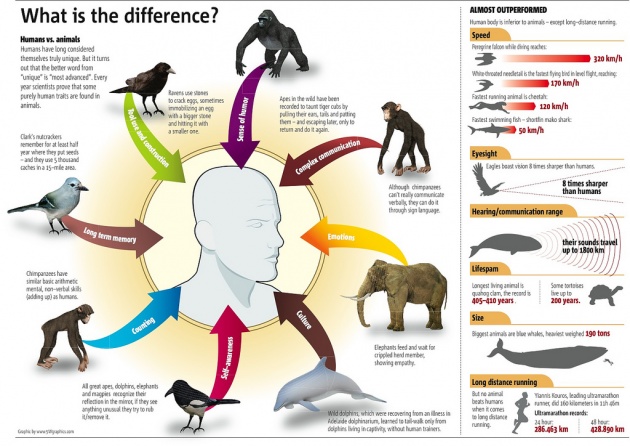
This image is property of cdn.bitlanders.com.
Aesthetic Appreciation and Creation
Human ability to appreciate and create art
Humans possess a unique ability to appreciate and create art, setting us apart from other animals. Art encompasses various forms of expression, including visual arts, literature, music, dance, theater, and film. Humans are not only capable of recognizing and appreciating aesthetic qualities but also of actively producing creative works.
The creation and appreciation of art are deeply ingrained in human culture and have been integral to our social, emotional, and intellectual development throughout history. Art allows us to explore and represent our experiences, emotions, and ideas, transcending language barriers and connecting us on a fundamental level. It serves as a medium for self-expression, cultural preservation, and social critique.
Role of aesthetics in human culture and behavior
Aesthetics, the study of beauty and the principles of art, have a profound impact on human culture and behavior. The perception of beauty varies across individuals and cultures, influenced by a combination of biological, psychological, and cultural factors. Aesthetic preferences shape our choices, beliefs, and social identities.
Artistic expressions and aesthetic experiences elicit emotional and cognitive responses, fostering empathy, reflection, and inspiration. They can uplift spirits, provoke thought, or challenge societal norms. The role of aesthetics in human culture and behavior reflects our capacity for creativity, imagination, and the pursuit of beauty and meaning.
Expression of human experience through art and literature
Art and literature serve as powerful mediums for expressing the complexity of the human experience. Through creative works, humans can represent and explore a range of emotions, perspectives, and cultural themes. Artistic expressions often reflect societal values, concerns, and aspirations, shedding light on the diverse dimensions of human existence.
Literature, in particular, provides a means to tell stories, share knowledge, and engage in introspection. It allows us to delve into the depths of human nature, confront ethical dilemmas, and grapple with existential questions. By engaging with art and literature, humans gain insight into the lives of others and expand their understanding of the world.
Complex Cognitive Abilities
Advanced problem-solving skills
Humans possess advanced problem-solving skills that differentiate us from other animals. Our cognitive abilities enable us to analyze complex situations, consider multiple factors, and generate creative solutions. We can apply abstract reasoning and critical thinking to overcome challenges and adapt to new circumstances.
These problem-solving skills have been fundamental to human survival and progress throughout history. From devising strategies for hunting and gathering to solving complex mathematical equations, humans have continually used their cognitive abilities to overcome obstacles, improve living conditions, and expand knowledge.
Ability to learn and adapt
Humans have a remarkable capacity for learning and adaptation. We can acquire new knowledge, skills, and behaviors through education, observation, and experience. This ability to learn and adapt allows us to thrive in diverse environments and respond to changing circumstances.
Through learning, humans accumulate information, refine their cognitive abilities, and develop expertise in various domains. We can adapt our behaviors, strategies, and beliefs based on new information and changing contexts. The ability to learn and adapt has been critical for human progress, enabling us to evolve, innovate, and navigate the complexities of the world.
Capacity for abstract thinking and imagination
One of the distinguishing features of human cognition is our capacity for abstract thinking and imagination. Humans can engage in hypothetical reasoning, conceptualize ideas, and envision possibilities that go beyond the immediate reality. This ability allows us to explore alternative scenarios, engage in creative problem-solving, and conceive of novel concepts and theories.
Abstract thinking and imagination have been instrumental in human scientific, artistic, and philosophical pursuits. They have fueled our discoveries, inventions, and interpretations of the world. Our capacity for abstract thinking and imagination reflects our cognitive flexibility and creativity, contributing to our unique intellectual capabilities.

This image is property of www.thoughtco.com.
Ethics and Moral Reasoning
Development of ethical principles and moral codes
Humans have developed ethical principles and moral codes that guide our behaviors, interactions, and decision making. Ethical principles provide a framework for determining what is right or wrong, just or unjust, and have evolved over time across different cultures and societies.
The development of ethical principles reflects our unique capacity for moral reasoning, the ability to evaluate actions in terms of their perceived moral value. Moral reasoning considers factors such as fairness, justice, empathy, and the well-being of others. It involves the application of ethical principles to real-life situations, requiring thoughtful consideration and reflection.
Role of ethics and morality in human society
Ethics and morality have a profound impact on human society. They form the foundation of social norms, legal systems, and moral frameworks that guide our interactions and behaviors. Ethical considerations influence our relationships, social institutions, and the distribution of resources and opportunities.
Ethics and morality play a crucial role in promoting cooperation, trust, and social cohesion. They inform our decisions and actions in both personal and public contexts, shaping the well-being and progress of societies. The recognition and enforcement of ethical principles acknowledge our responsibility towards others and demonstrate our moral agency.
Influence of moral reasoning on human decision making
Moral reasoning plays a significant role in human decision making. Our moral judgments and values influence the choices we make and the actions we take in everyday life. Ethical considerations guide our behaviors, helping us navigate complex dilemmas and make decisions that align with our values and moral beliefs.
Moral reasoning can vary across individuals and cultures, reflecting different ethical frameworks and priorities. It involves weighing different interests, considering the consequences of our actions, and reflecting on the principles that guide our moral compass. The influence of moral reasoning on human decision making underscores our capacity for moral agency and the recognition of ethical obligations.
Long Childhood and Learning Period
Prolonged dependency of human offspring
Humans have a uniquely long period of dependency and learning compared to other animals. Human offspring require extensive care and nurturing from caregivers, often spanning over a decade or more. This prolonged period of dependency allows for extensive learning opportunities, skill development, and socialization.
The extended childhood and learning period contribute to the transmission of cultural knowledge, the acquisition of language, and the development of social, emotional, and cognitive abilities. The support and guidance provided by caregivers play a crucial role in shaping the development and well-being of individuals throughout their lives.
Role of learning and education in human life
Learning and education play vital roles in the lives of humans. From early childhood to adulthood, humans engage in continuous learning to acquire knowledge, develop skills, and expand their understanding of the world. Education systems provide formal structures and processes to facilitate learning, supporting intellectual, social, and emotional development.
Learning extends beyond formal education to include informal and lifelong learning experiences. Humans have a natural curiosity and a drive to explore and understand their environment. Learning allows us to adapt to new situations, engage in critical thinking, and navigate the complexities of the modern world. The role of learning and education in human life signifies our capacity for intellectual growth, personal development, and societal progress.
Impact of upbringing and environment on human development
Upbringing and environmental factors significantly influence human development. The experiences, interactions, and environments in which individuals grow up shape their physical, cognitive, emotional, and social development.
Children learn from the caregivers, family members, and communities around them, internalizing social norms, values, and behaviors. The quality of early experiences, such as nutrition, care, and stimulation, can have long-lasting effects on cognitive and physical health. Environmental factors, such as socioeconomic status, access to education, and community resources, also impact individuals’ opportunities and well-being.
Recognizing the impact of upbringing and environment on human development highlights the interplay between nature and nurture in shaping human characteristics and abilities. It underscores our plasticity, adaptability, and the importance of providing supportive and nurturing environments for individuals to thrive.
In conclusion, humans possess a myriad of unique qualities that distinguish us from other animals. Our advanced communication skills, complex emotions, self-awareness, reliance on tools and technology, cultural adaptation, reliance on social structures, aesthetic appreciation, complex cognitive abilities, ethics and moral reasoning, as well as our long childhood and learning period, collectively contribute to what makes us uniquely human. These characteristics have played essential roles in our survival, progress, and the development of rich and diverse societies. Understanding and appreciating our distinct qualities can shed light on the complex nature of human beings and our place in the world.






